1. Introduction of circular knitting machine technology
1. Brief introduction of circular knitting machine
The circular knitting knitting machine (as shown in Figure 1) is a device that weaves cotton yarn into tubular cloth. It is mainly used to knit various types of raised knitted fabrics, T-shirt fabrics, various patterned fabrics with holes, etc. According to the structure, it can be divided into single jersey circular knitting machine and double jersey circular knitting machine, which are widely used in the textile industry.
(1) The inverter is required to have strong environmental resistance, because the temperature of the on-site working environment is relatively high, and cotton wool can easily cause the cooling fan to stall and be damaged, and the cooling holes to be blocked.
(2) Flexible inching operation function is required. Inching buttons are installed in many places of the equipment, and the inverter is required to respond quickly.
(3) There are three speeds required in speed control. One is the inching operation speed, usually around 6Hz; the other is the normal weaving speed, with the highest frequency up to 70Hz; the third is the low-speed gathering operation, which requires a frequency of about 20Hz.
(4) During the operation of the circular knitting machine, motor reversal and rotation are absolutely prohibited, otherwise the needles of the needle bed will be bent or broken. If the circular knitting machine uses a single-phase bearing, this will not be considered. If the system rotates forward and reverse It completely depends on the forward and reverse rotation of the motor. On the one hand, it needs to be able to prohibit reverse rotation, and on the other hand, it needs to set up DC braking to eliminate rotation.
3. Performance requirements
When weaving, the load is heavy, and the inching/starting process needs to be quick, which requires the inverter to have low frequency, large torque, and fast response speed. The frequency converter adopts vector control mode to improve the motor’s speed stabilization accuracy and low-frequency torque output.
4. Control wiring
The control part of the circular knitting knitting machine adopts microcontroller or PLC + human-machine interface control. The frequency converter is controlled by terminals to start and stop, and the frequency is given by analog quantity or multi-stage frequency setting.
There are basically two control schemes for multi-speed control. One is to use analog to set the frequency. Whether it is jogging or high-speed and low-speed operation, the analog signal and operating instructions are given by the control system; the other is to use a frequency converter. The built-in multi-stage frequency setting, the control system gives multi-stage frequency switching signal, the jog is provided by the inverter itself, and the high-speed weaving frequency is given by analog quantity or digital setting of the inverter.
2. On-site requirements and commissioning plan
(1) On-site requirements
The circular knitting machine industry has relatively simple requirements for the control function of the inverter. Generally, it is connected to terminals to control start and stop, analog frequency is given, or multi-speed is used to set the frequency. Inching or low-speed operation is required to be fast, so the inverter is required to control the motor to generate large low-frequency torque at low frequency. Generally, in the application of circular knitting machines, the V/F mode of the frequency converter is sufficient.
(2) Debugging scheme The scheme we adopt is: C320 series sensorless current vector inverter Power: 3.7 and 5.5KW
3. Debugging parameters and instructions
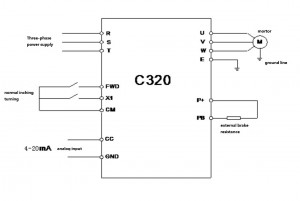
1. Wiring diagram
2. Debug parameter setting
(1) F0.0=0 VF mode
(2) F0.1=6 frequency input channel external current signal
(3) F0.4=0001 External terminal control
(4) F0.6=0010 reverse rotation prevention is valid
(5) F0.10=5 acceleration time 5S
(6) F0.11=0.8 deceleration time 0.8S
(7) F0.16=6 carrier frequency 6K
(8) F1.1=4 Torque boost 4
(9) F3.0=6 Set X1 to forward jog
(10) F4.10=6 set the jog frequency to 6HZ
(11) F4.21=3.5 Set the jog acceleration time to 3.5S
(12) F4.22=1.5 sets the jog deceleration time to 1.5S
Debugging Notes
(1) First, jog to determine the direction of the motor.
(2) Regarding the problems of vibration and slow response during jogging, the acceleration and deceleration time of jogging needs to be adjusted according to requirements.
(3) Low-frequency torque can be improved by adjusting the carrier wave and torque boost.
(4) Cotton wool blocks the air duct and the fan stalls, causing poor heat dissipation of the inverter. This situation occurs frequently. At present, the general inverter skips the thermal alarm and then manually removes the lint in the air duct before continuing to use it.
Post time: Sep-08-2023